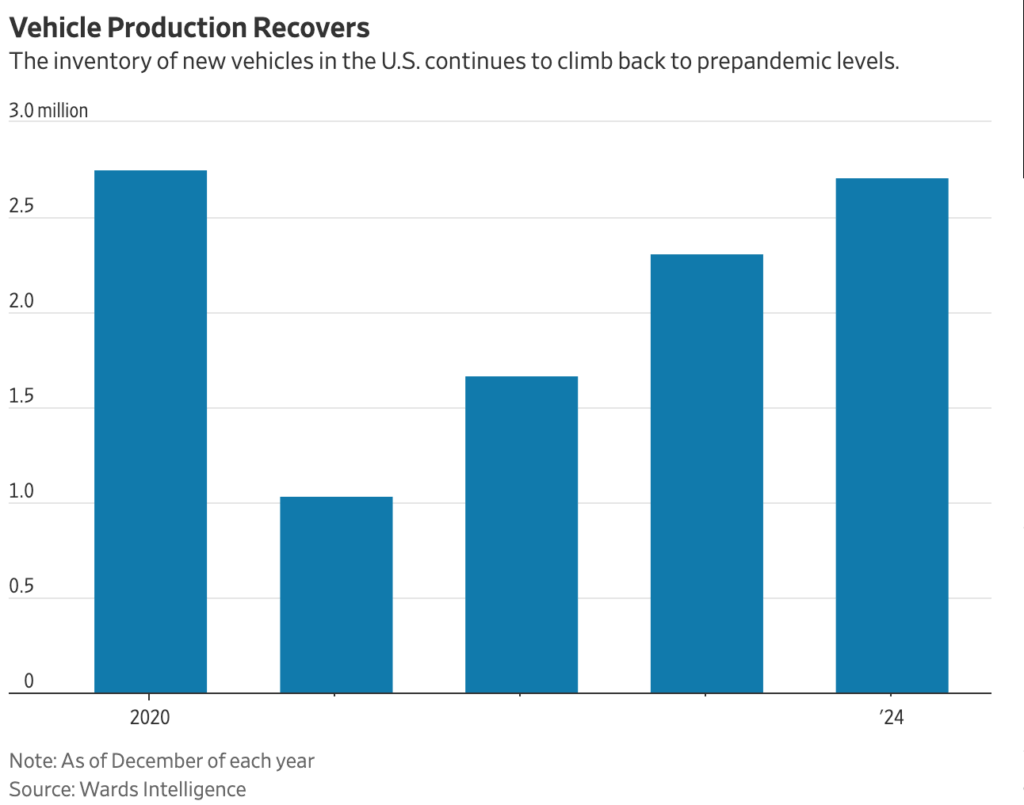
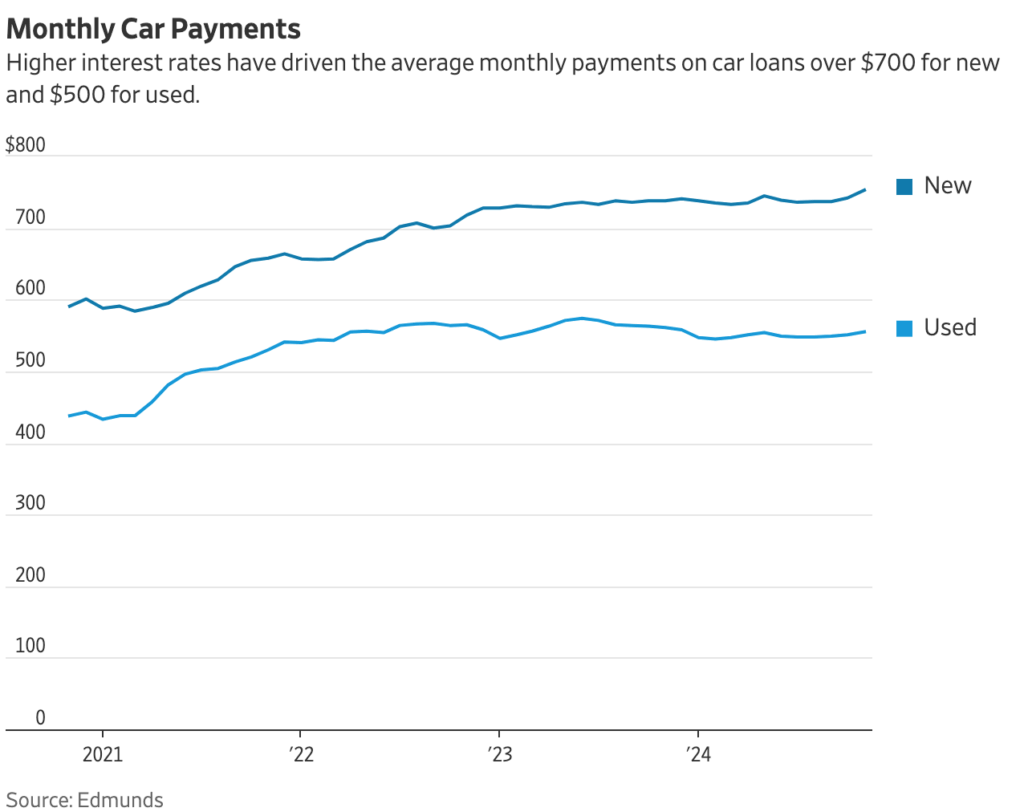
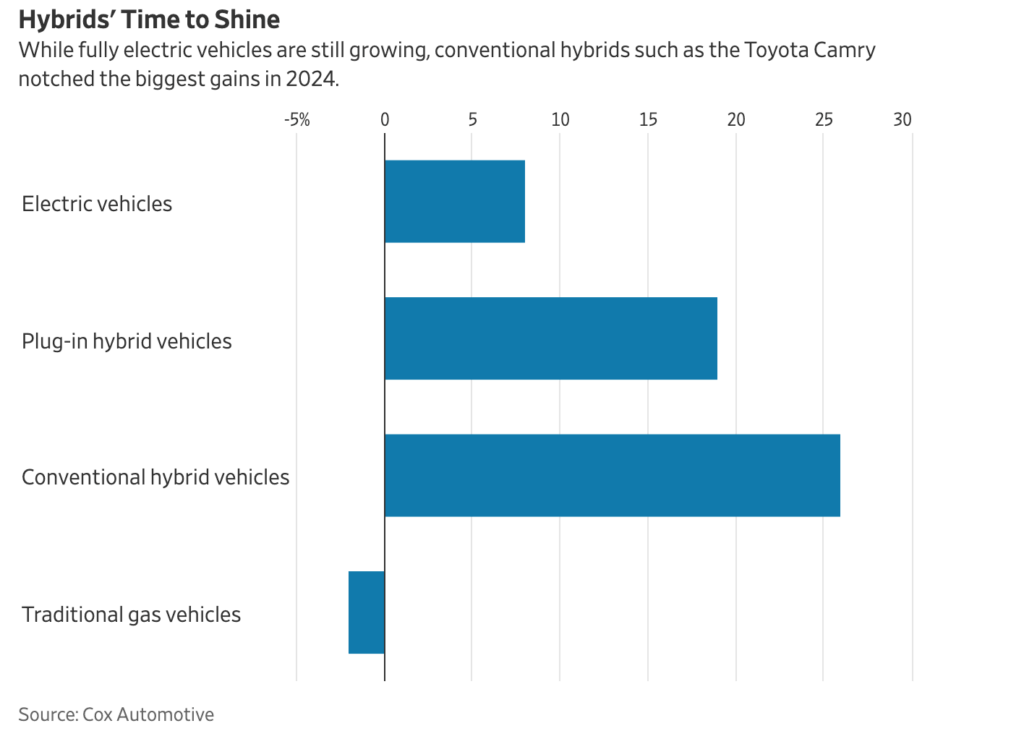
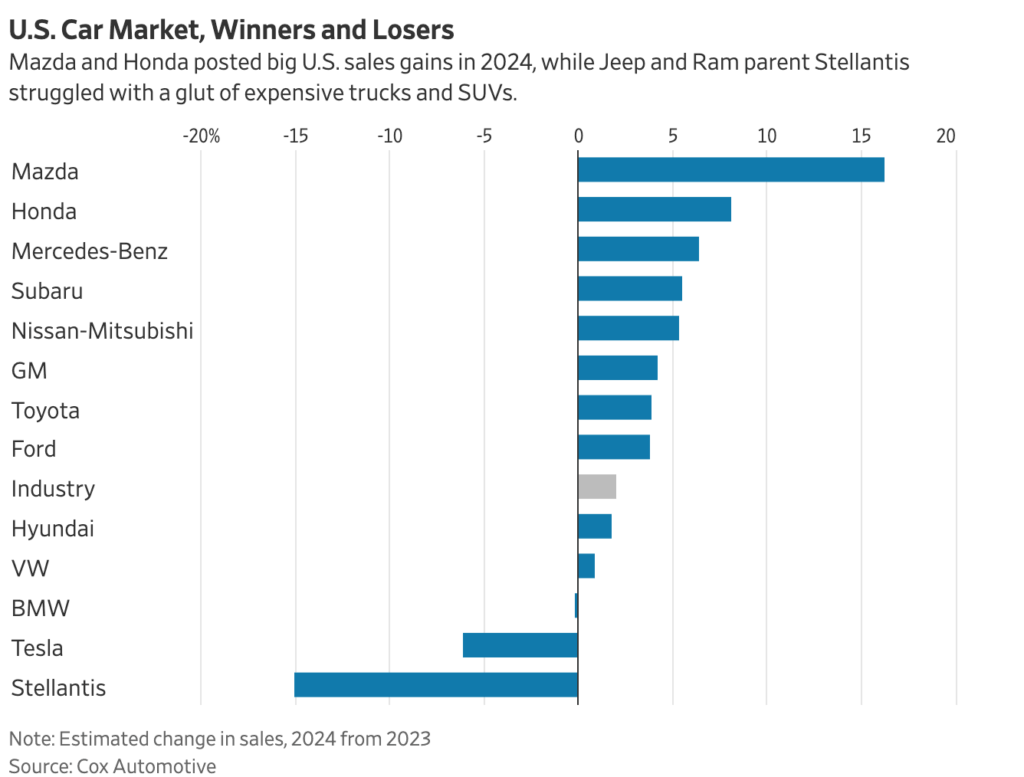
Major auto-exporting nations are in crisis mode after President Trump announced new 25 percent tariffs on imported cars and auto parts, starting April 3, that will hit popular brands from Toyota to Porsche.
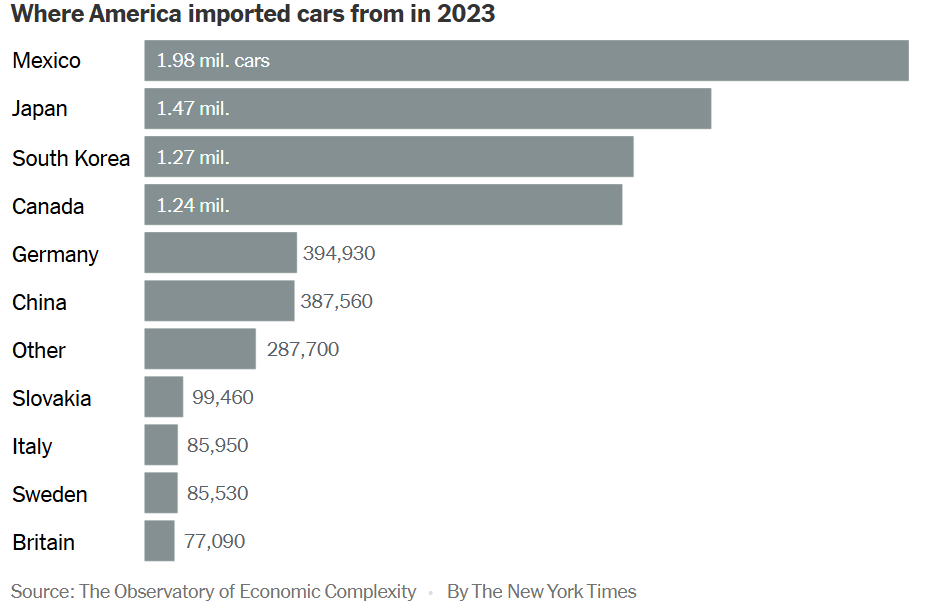
Nearly half of new passenger vehicles sold in the U.S. in 2024 were assembled outside the U.S., according to data from S&P Global Mobility. Most come from five nations: Mexico, Japan, South Korea, Canada and Germany.

Economic driver
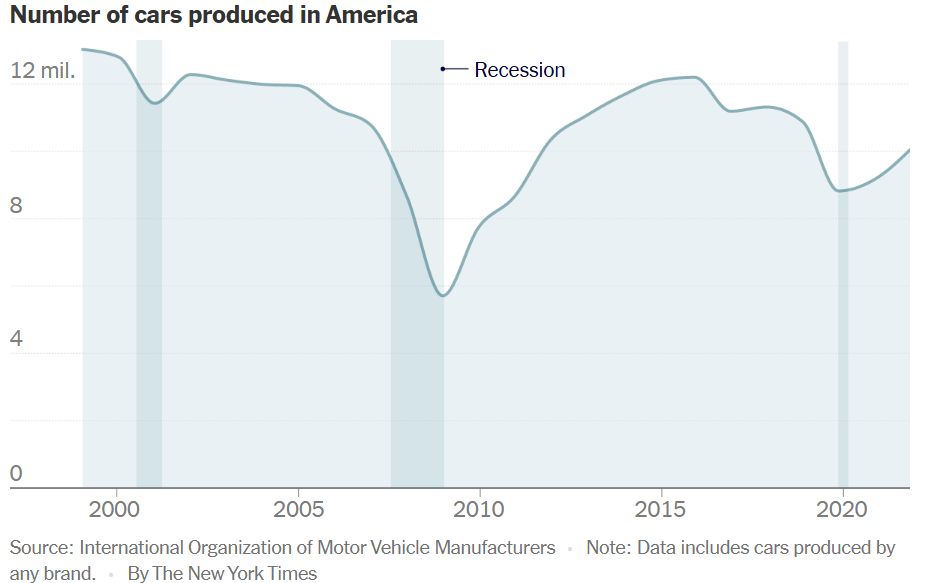
Cars drive the economies of these nations and typically account for a big proportion of exports.
U.S. auto tariffs could reduce economic growth in Japan by 0.2 percentage point, said Takahide Kiuchi, executive economist at Nomura Research Institute. If Japanese carmakers shift production to the U.S., they would maintain sales but “it would be a headwind for the Japanese economy,” he said.

The automotive industry is also a linchpin of the European economy, accounting for 7 percent of the European Union’s economic output. For Germany, auto exports to the U.S. account for close to half a percent of value added in the economy, according to Capital Economics.
The impact of tariffs would stretch deep into the German supply chain. Roughly a third of small and midsize automotive suppliers surveyed by the country’s automotive trade association last month expected to be directly affected by U.S. tariffs.
More than a dozen global automakers operate close to 40 plants in Mexico, including General Motors, Mercedes-Benz, BMW, Hyundai and Toyota. The country exported almost three million vehicles to the U.S. and supplied 40 percent of U.S. auto parts last year. Close to two million Mexicans work in the vehicle and auto-parts industries, with exports last year close to $200 billion.
Brian Kingston, the head of the Canadian Vehicle Manufacturers’ Association, said there has been more than $280 billion of investment in the North American auto industry since 2020, most of which was in the U.S. and all of which was done under the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement that Trump signed in 2018. Canada’s auto sector employs more than 125,000 people and produced roughly 1.3 million cars last year, most of which were exported to the U.S.
Big exporters
The world’s biggest carmaker, Toyota, shows how the industry relies on exports to the U.S. American showrooms for Toyota feature Prius hybrids made in Japan, RAV4 sport-utility vehicles made in Canada and Tacoma pickups from Mexico.
Last year, Toyota sold 2.3 million vehicles in the U.S. About a quarter of those vehicles came from Japan, and an additional quarter or so were shipped from Canada and Mexico. The remaining half were built in the U.S., a Toyota spokesman said.
Many non-U. S. automakers get a quarter or more of their sales in the U.S.

rump said he wanted the carmakers to move their production to the U.S. Hyundai said at the White House on Monday that it would invest an additional $21 billion in U.S.-based car manufacturing and supply chains for critical materials, including a $5.8 billion steel mill to be built in Louisiana.
German luxury brands Mercedes-Benz and BMW have developed manufacturing bases for sport-utility vehicles in the U.S. in recent decades, but they continue to ship sedans across the Atlantic as well as engines and transmissions for the SUVs.
All the vehicles sold in the U.S. by Audi and Porsche, both owned by Volkswagen, are imported. Honda’s exports to the U.S. include the made-in-Canada CR-V and Civic and Mexico-produced HR-V. Hyundai’s exports include the hybrid Tucson and Palisade SUV.
Governments hit back
South Korea said it planned emergency support for the auto industry. Trade minister Ahn Duk-geun said the industry faced “considerable damage.” Japan said it would ask Trump for a tariff exemption, and Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba said retaliation was an option.
In Brussels, European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen condemned the tariffs as “bad for businesses, worse for consumers,” while saying the EU would seek negotiated solutions.
German Economy Minister Robert Habeck said the EU should respond decisively and “not give in to the U.S.”
In Mexico, the government plans to step up efforts to obtain preferential tariff treatment from the U.S., particularly in the automotive sector where both countries are highly integrated. “What we are looking for is that the products made in Mexico ultimately have a better price than any other country—such as Germany, Japan, South Korea—that also exports to the U.S.,” Economy Minister Marcelo Ebard said Thursday.
One Canadian government official said that Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick reached out to Doug Ford, the leader of the province of Ontario, and suggested that Canada could get a break on the tariffs that Trump announced on Wednesday.